Codux Help Center
Browse our articles to find the answers you need
Clone a Git Repository
When you clone a Git repository, you'll be asked for the repository URL, and to provide a local path to clone it to.
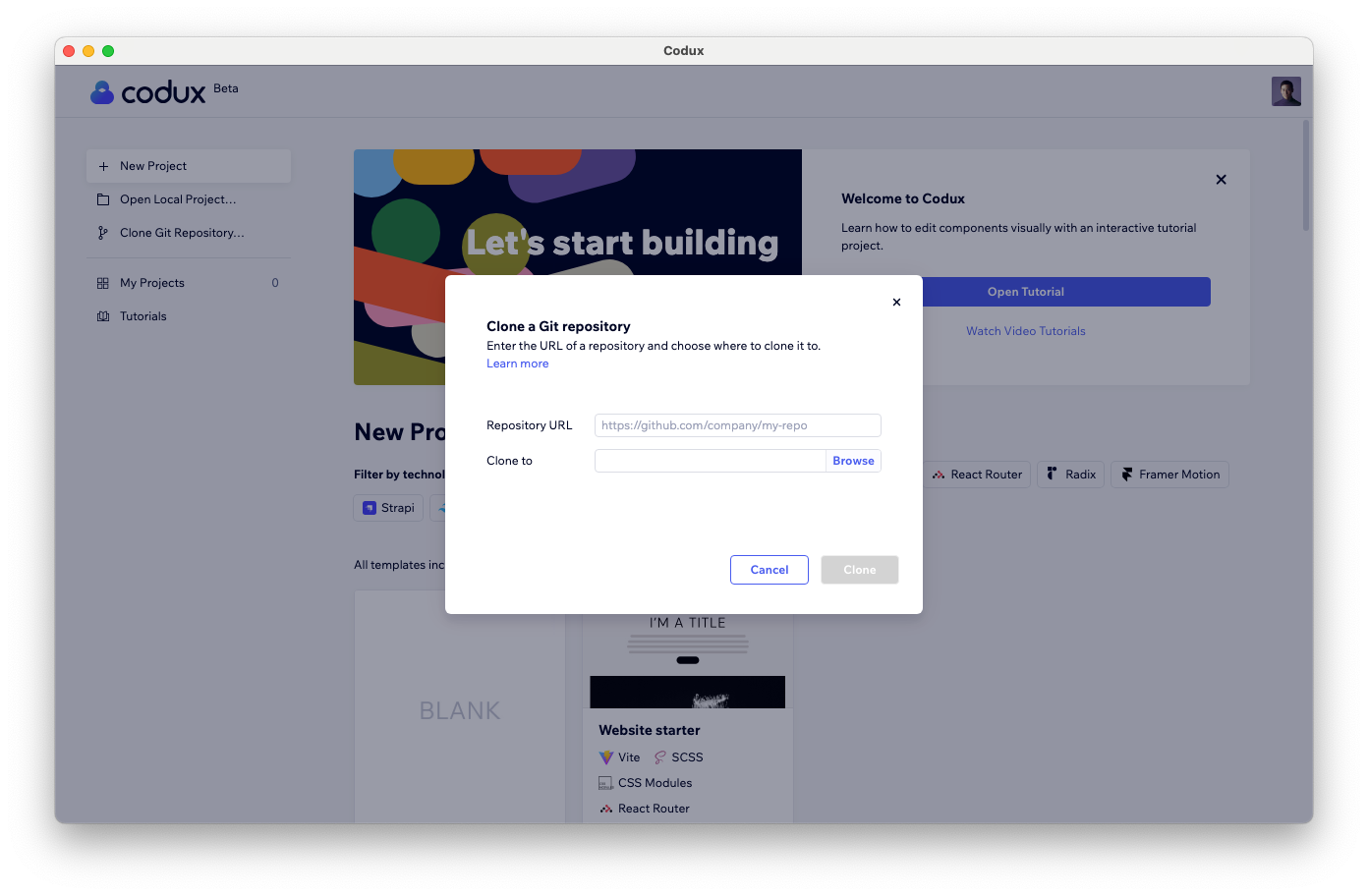
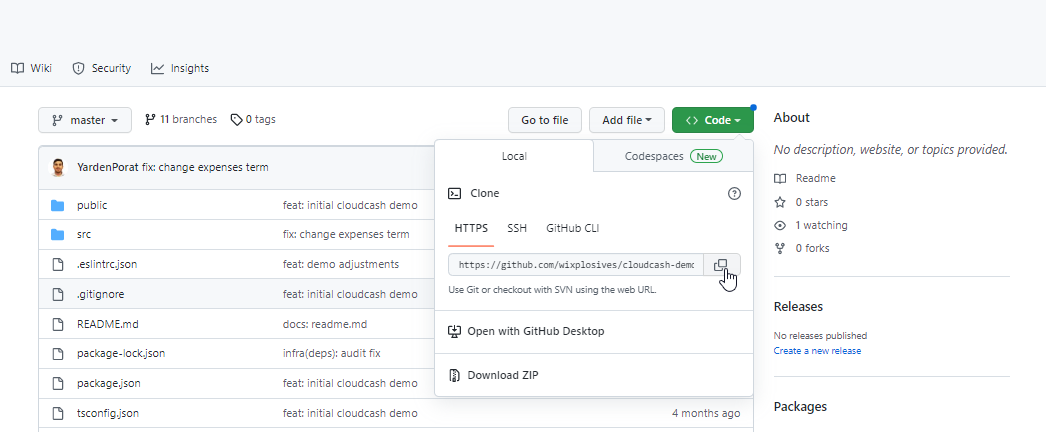
You can get the URL from the repo on GitHub or from the project owner.
After filling in these fields, click Clone.
Important!
To add a private GitHub project to Codux or sync one to or from GitHub, you'll first need to sign in to your GitHub account with the appropriate permissions for the repository (if you haven't logged in already). Codux will prompt you when this is needed, but you can also find the login option in the menu at the top right of the screen.
If all goes well, and you have the correct permissions, you'll see a message stating that the project cloned successfully. From there, click Open.
As this is the first time that the project opened, a quick housekeeping task needs to be completed – a script needs to install required dependencies (other pieces of code needed to make everything look right) on your computer. Don't fret though — just click Install when prompted.
Refer to Project Prerequisites and Dependencies to check that your project meets the requirements.
Cloning a non-GitHub remote project
If you're cloning a project from a non-GitHub remote provider (such as GitLab) and it's a private project, you'll need to do it by SSH rather than HTTPS. This requires you to create an SSH key on your computer to authenticate with the repository, and then use the project's SSH link.
If it's a public project, you can clone it by HTTPS like you would a GitHub project, but you'll only have basic Git functionality.
Here's where you can copy an SSH key in GitLab:
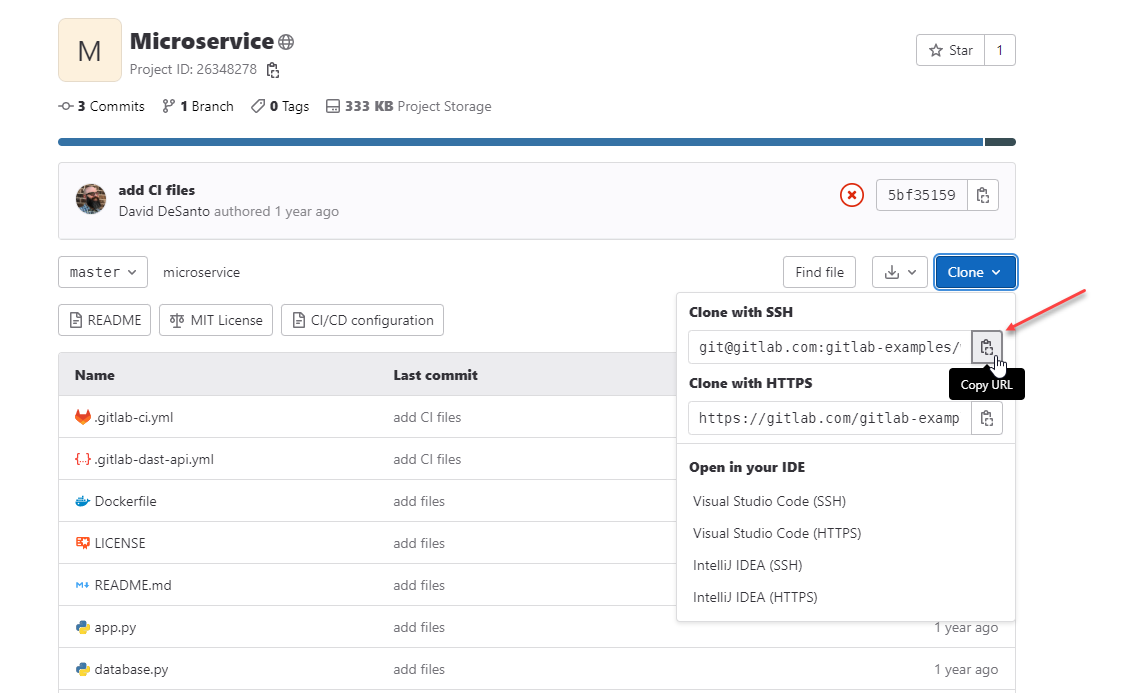
Until you set up the SSH key, you won't be able to sync with the repository (publish branches, push changes, etc.).
Important!
If you're cloning a BitBucket repository using an SSH key, you need to add "bitbucket.org" to the list of known hosts.
Was this article helpful?